Drug Driving Detection: How Will Police Test?
Did you know that across Canada, police have been trained to detect if a driver is under the influence of a drug? With the recent legalization of cannabis and the rise in drug-impaired driving incidents, law enforcement agencies have implemented new measures to ensure road safety.
In accordance with the Cannabis Act, police can now use approved drug screening devices to detect the recent presence of drugs such as THC, cocaine, and methamphetamine. But how will the police test drivers for drug impairment? Let’s explore the methods and procedures involved in drug driving detection.
Key Takeaways:
- Across Canada, police are trained to detect drug-impaired driving.
- The Cannabis Act allows police to use approved drug screening devices.
- Roadside tests and further testing at the police station are conducted to determine impairment.
- Penalties for drug-impaired driving can include fines, imprisonment, and license suspensions.
- The Government of Canada has implemented stronger laws to address drug-impaired driving.
Roadside Testing: Standardized Field Sobriety Test (SFST)
A Standardized Field Sobriety Test (SFST) is a protocol used by law enforcement officers to assess whether a driver is impaired by drugs. The SFST consists of a series of tests and observations conducted at the scene of a traffic stop.
The purpose of the SFST is to evaluate a driver’s physical and cognitive abilities and gather evidence of impairment. These tests are standardized, meaning that they follow a specific set of instructions and criteria to ensure consistency and accuracy.
During an SFST, an officer may ask the driver to perform various tasks, such as:
- Walking in a straight line, heel to toe
- Standing on one leg for a certain period
- Turning around and changing direction
The officer will closely observe the driver’s performance, looking for signs of impairment such as lack of balance, difficulty in following instructions, or the inability to maintain proper coordination.
It’s important to note that the results of the SFST cannot be used as grounds to lay a charge or used as evidence in a criminal trial. However, if a driver fails the SFST, it gives the officer reasonable grounds to demand further testing, such as drug impairment testing or an oral fluid sample, at the police station.

Roadside Testing: Oral Fluid (Saliva) Sample Testing
When it comes to detecting drug-impaired driving, police officers have several tools at their disposal. One of these tools is the ability to demand an oral fluid sample from a driver if they have reasonable suspicion that drugs are present in their system. This oral fluid drug screening test can help determine if a driver has recently consumed certain drugs, such as THC, which is the psychoactive component of cannabis.
Reasonable suspicion can be based on various factors, including erratic driving, red eyes, muscle tremors, and unusual speech patterns. If a driver exhibits these signs, a police officer may request an oral fluid sample to further assess the presence of drugs.
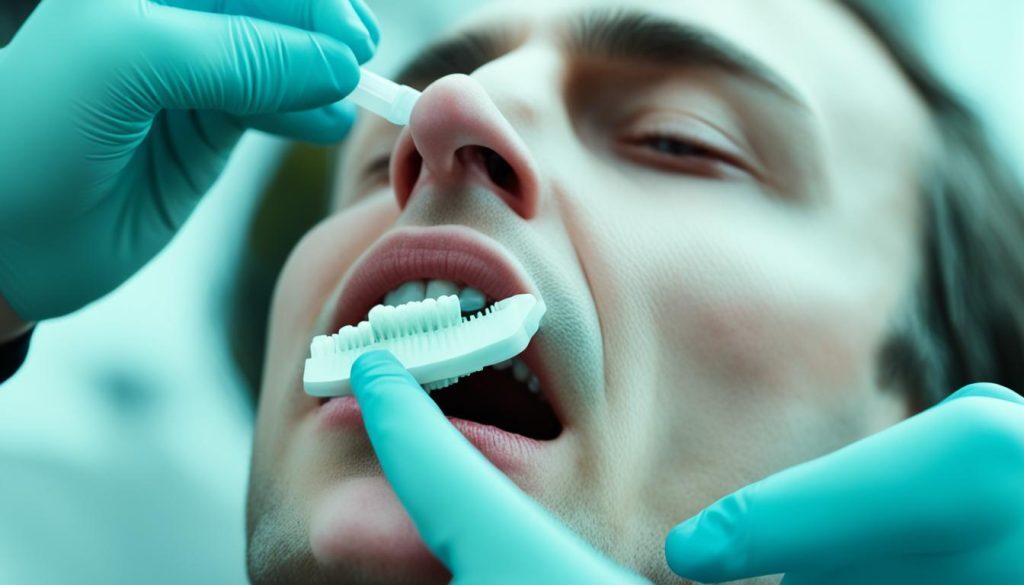
The oral fluid drug screening test is a non-invasive procedure that involves collecting a saliva sample from the driver. This sample is then tested using specialized equipment that can detect the presence of drugs. The results of this test can provide valuable evidence of recent drug use, particularly THC, which can impair a driver’s ability to operate a motor vehicle safely.
If the oral fluid drug screening test yields a positive result, indicating the presence of drugs, it may provide sufficient grounds for the police to demand further testing at the police station. This additional testing can involve more comprehensive assessments, such as a drug recognition evaluation (DRE), which is conducted by a trained drug recognition expert (DRE).
Drug Recognition Experts Protocol
The drug recognition experts protocol is a standardized procedure followed by trained officers known as drug recognition experts. These experts are highly skilled in identifying signs and symptoms of drug impairment. The protocol includes a series of assessments, including physical examinations, coordination tests, and evaluations of pupil size, blood pressure, and pulse rate, among others.
The drug recognition experts protocol aims to provide a comprehensive evaluation of a driver’s impairment level and determine if their ability to operate a motor vehicle has been adversely affected by drugs.
By employing the oral fluid drug screening test and the drug recognition experts protocol, law enforcement can effectively detect and address drug-impaired driving, helping to safeguard the roads and promote safe driving practices.
Testing at the Police Station: Drug Recognition Evaluation (DRE)
If a driver fails a roadside test or provides a positive oral fluid sample, they may be taken to a police station for further testing. At the police station, a trained officer known as a drug recognition expert (DRE) can conduct a drug recognition evaluation (DRE) on the driver. This evaluation involves a series of tests, including sobriety tests similar to the SFST, as well as clinical tests such as checking blood pressure, body temperature, pulse rate, and measuring pupil size. The results of the DRE can be used as evidence in a criminal trial if the officer believes the driver’s ability to operate a motor vehicle has been impaired by drugs.
During the drug recognition evaluation, the trained officer follows a standardized protocol that includes conducting a thorough examination of the driver’s physical appearance and behavior. This includes assessing factors such as bloodshot or watery eyes, muscle tremors, and erratic speech patterns. The officer will also evaluate the driver’s coordination by conducting various field sobriety tests to determine impairment.
Drug Recognition Experts Protocol:
- Checking blood pressure, body temperature, and pulse rate
- Measuring pupil size in different lighting conditions
- Assessing vital signs and physical coordination
- Conducting additional tests to identify the specific drug category responsible for impairment
Based on the findings of the drug recognition evaluation, the officer may request further testing, such as a blood or bodily fluid sample, to confirm the presence of drugs in the driver’s system. The results of these tests can provide conclusive evidence of drug impairment and can be used in court proceedings.
Testing at the Police Station: Breath Sample – Evidentiary Breath Test
In addition to the Drug Recognition Evaluation (DRE), police officers may request a breath sample from the driver for an evidentiary breath test. This test is primarily used to detect the presence of alcohol in the driver’s system, but it can also help rule out impairment by alcohol when drug impairment is suspected.
The evidentiary breath test is typically conducted at the police station or a medical facility and is considered a reliable method for determining a driver’s breath alcohol concentration (BrAC). The results of this test can be used as admissible evidence in a criminal trial.
During the evidentiary breath test, the driver is required to blow into a specialized device known as a breathalyzer. This device measures the amount of alcohol present in the breath and provides an estimate of the driver’s blood alcohol concentration (BAC).
The breathalyzer works by measuring the alcohol content in the driver’s breath sample and converting it into a numerical value, typically expressed as a percentage of alcohol in the blood. The legal limit for blood alcohol concentration (BAC) in Canada is 0.08%, which means that a driver with a BAC level equal to or higher than 0.08% is considered impaired.
It is important to note that the evidentiary breath test is specifically designed to detect alcohol and cannot directly determine the presence of drugs in the driver’s system. If drug impairment is suspected, additional testing methods such as the DRE or bodily fluid samples may be utilized to gather evidence.
| Advantages of Evidentiary Breath Test | Limitations of Evidentiary Breath Test |
|---|---|
|
|
Testing at the Police Station: Bodily Fluid Samples
In addition to other tests conducted at the police station, bodily fluid samples may be requested from the driver to confirm or negate the findings of previous tests.
Blood samples are typically taken to determine both blood-alcohol concentration (BAC) and blood-drug concentration. This type of testing is highly accurate and can provide valuable evidence of drug presence in the driver’s system.
Urine and saliva samples may also be collected at the police station. These samples are often used to confirm the results of a Drug Recognition Evaluation (DRE) and provide further evidence of drug impairment.
Advantages of Bodily Fluid Testing
Bodily fluid testing offers several advantages for detecting drug presence and impairment:
- Accurate detection: Blood testing can accurately determine the concentration of drugs in the bloodstream, providing objective evidence of impairment.
- Confirmation of results: Urine and saliva testing can confirm the findings of other tests, such as the DRE, by detecting the presence of drugs in the driver’s system.
- Non-invasive procedure: Collecting bodily fluid samples is a relatively non-invasive procedure that can be performed at the police station.
When conducted by trained professionals, bodily fluid testing can provide reliable evidence of drug presence and impairment, supporting the police’s efforts to ensure road safety.
Related Offences and Penalties
When it comes to drug-impaired driving, the consequences can be severe. Depending on the findings of the police and the results of the drug driving testing methods, a driver may face criminal charges for various offences. These offences can include:
- Impaired driving
- Driving over the legal blood-alcohol limit
- Failure to comply with a demand for a sample or test
If found guilty of these offences, drivers can face a range of penalties. This can include hefty fines, imprisonment, license suspensions, and even mandatory participation in education and interlock programs. It is crucial for drivers to understand the potential consequences of drug-impaired driving and take the necessary precautions to ensure their own safety and the safety of others on the road.
Take a look at the table below for a summary of the related offences and penalties:
It is essential to note that these penalties can vary depending on the region and the specific circumstances of the case. Therefore, it is always advisable to consult with legal professionals to understand the legal implications in your jurisdiction.
How Recent Changes to the Criminal Code Address Drug-Impaired Driving
The Government of Canada has taken significant steps to address the serious issue of drug-impaired driving. With the implementation of stronger laws, they aim to deter and detect instances of drug impairment on the roads. These changes include the creation of new criminal offences for having prohibited blood drug concentrations within two hours of driving.
In addition, the government has authorized the use of drug screening equipment for roadside testing. This equipment enables law enforcement officers to effectively detect the presence of drugs in a driver’s system, ensuring the safety of all road users. By strengthening the existing legal framework for investigating and prosecuting drug-impaired driving, the government is sending a clear message that drug impairment will not be tolerated.
Understanding the severity of drug-impaired driving, the penalties for such offences can be significant. Offenders may face fines, imprisonment, and license suspensions depending on the specific nature of the offence. These penalties serve as a deterrent and emphasize the government’s commitment to keeping Canadians safe on the roads.
With these recent changes to the criminal code, Canada is taking a proactive approach to combat drug-impaired driving. By introducing stricter laws, authorizing drug screening equipment, and imposing penalties that reflect the seriousness of the offence, the government aims to create a safer and more responsible driving culture across the country.
- The Role of Police in Community Safety & Unity - October 6, 2025
- Quebec Police Officer Salary Insights 2023 - July 13, 2025
- Canada Arrest Protocol: What Police Say Upon Arrest - June 12, 2025



















Post Comment